As AI evolves from passive assistants to systems capable of autonomous reasoning, planning, and acting, the term “agentic AI” has gained traction. While they share some conceptual DNA, they are not synonymous. Understanding the distinction is crucial for developers building the next generation of intelligent systems.

In this article, we’ll clarify the difference between agentic AI and agents, and explore the practical impact on development, system design, and tool choices.
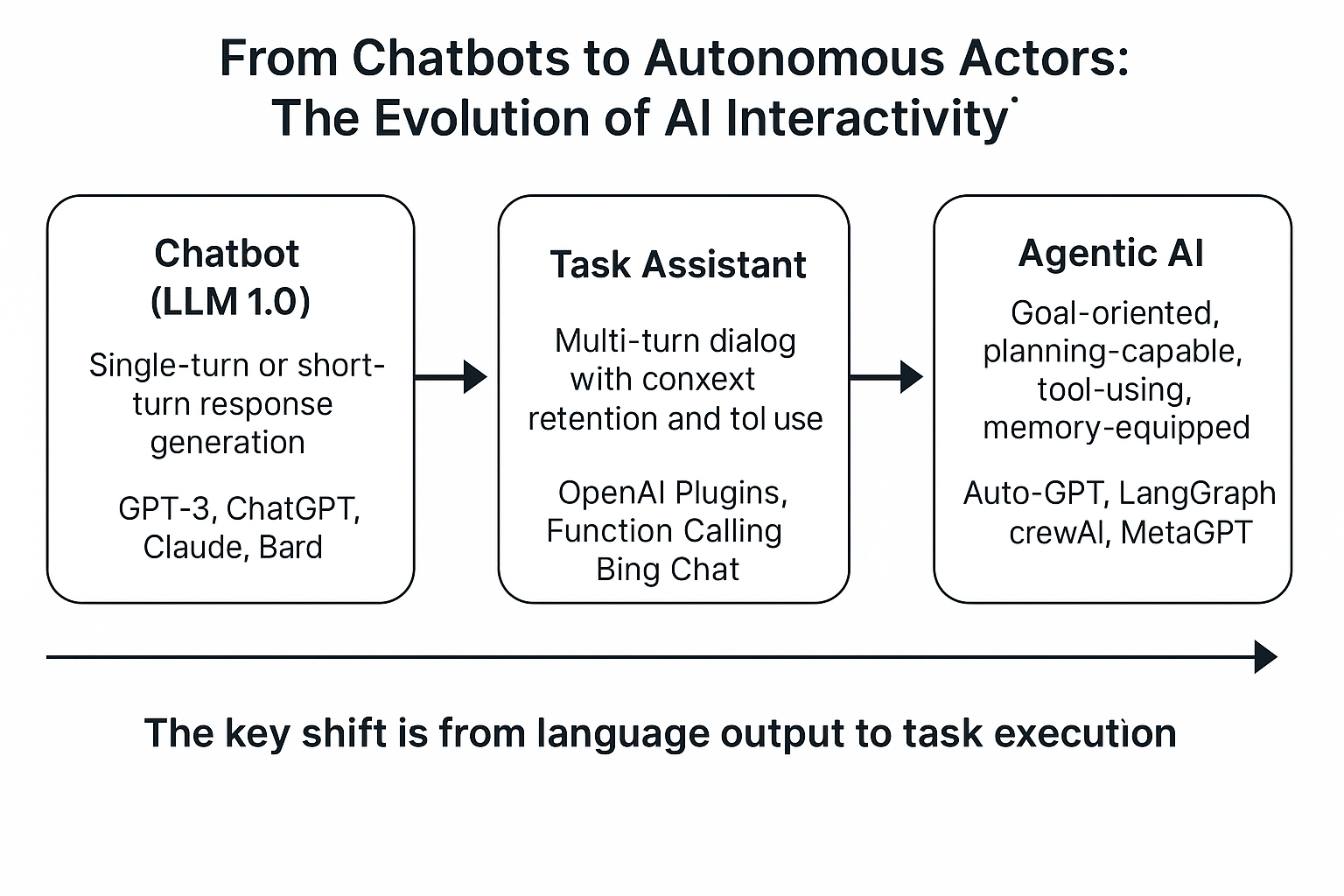
From Chatbots to Autonomous Actors: The Evolution of AI Interactivity
When GPT-3 came out, developers were amazed by how well it could chat and answer questions. Early tools built on it (like chatbots, assistants, and copilots) were mostly designed to respond to what users asked, without doing much more.
-
But in 2023 and 2024, the focus began to shift:
- Instead of just responding to commands, new AI systems began to initiate, plan, and carry out multi-step tasks.
- LLMs became capable of calling tools, querying databases, and looping through reasoning chains.
This marked the birth of agentic AI—where the model doesn’t just reply, it acts in a semi-autonomous way.
🤖 What Is an Agent?
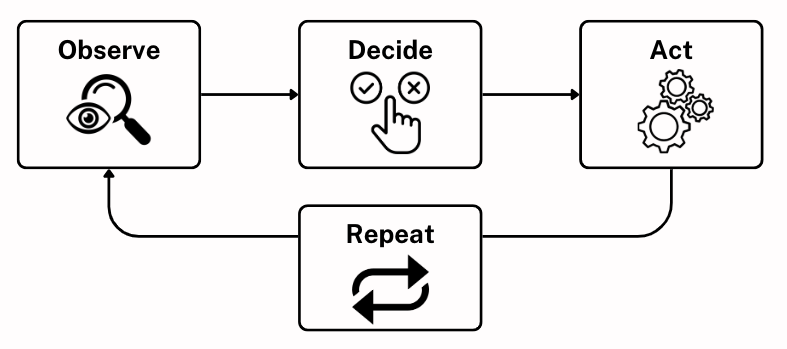
At its core, an agent is a software entity that perceives its environment, makes decisions, and acts to achieve specific goals. This concept has been around since the early days of artificial intelligence and appears in many contexts—from robotics and video games to enterprise software and distributed systems.
Most agents follow a basic loop:
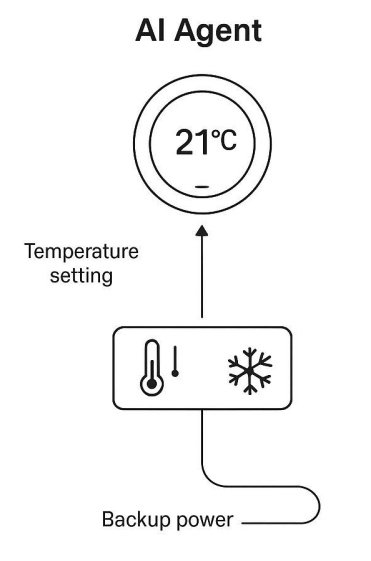
📌 Example: A smart thermostat observes the room temperature (Observe), compares it to the desired temperature (Decide), and turns the heater on or off (Act).
🧠 Types of Traditional Agents: Read This Article for a Comprehensive Guide to Traditional Agent Types (Read this article)
What is Agentic AI ?
Agentic AI refers to a new class of AI systems that go beyond simple interaction. They think, plan, act, and adapt. These systems are powered by large language models (LLMs) but are designed to operate more like autonomous problem-solvers than passive tools.
A typical agentic AI stack includes:
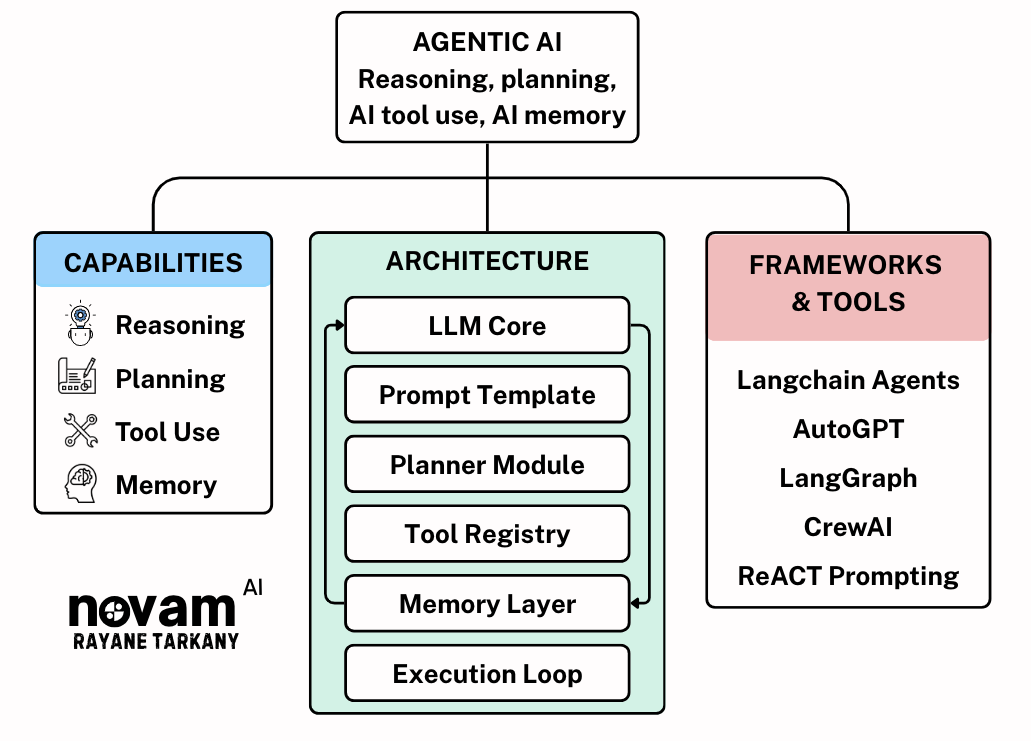
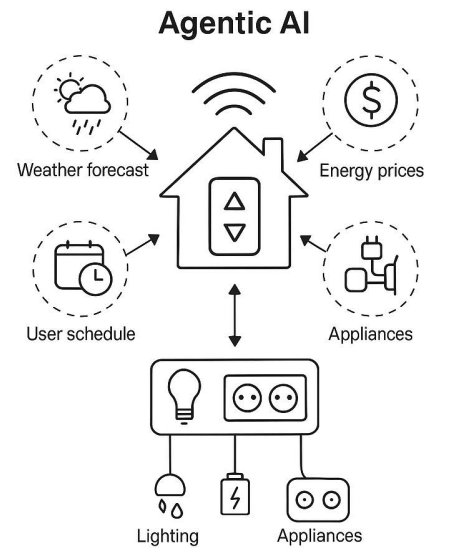
📌 Example:
-
The agentic system considers:
- Weather Forecast: Adjusts heating/cooling or lighting depending on conditions.
- Energy Prices: Optimizes energy usage to lower costs.
- User Schedule: Predicts when residents are home or away.
- Connected Appliances: Controls and syncs smart devices accordingly.
- Lighting & Power Control: Dynamically manages energy flow throughout the home.
Instead of fixed automation rules, the system reasons and decides based on context, goals, and current data: the essence of Agentic AI.
⚠️ Development Considerations
-
Agentic AI is powerful but non-deterministic, which introduces new challenges:
- Hallucinations: Agents may make up steps or tools
- Looping / Infinite Thinking: Without proper stop criteria, agents can get stuck
- Tool misuse: Choosing the wrong tool for a task
- Cost and latency: Each reasoning + tool step = multiple API calls
📄 Recommended Reading
“Agentic AI: A Framework for Building LLM-Powered Autonomous Agents”
For those who want to dive deeper into the architecture, reasoning capabilities, and design challenges of agentic systems, the paper Agentic AI: A Framework for Building LLM-Powered Autonomous Agents (May 2025) is a must-read.







Start the conversation